
Ideal antibody candidates are often required to bind with high affinity to a specific epitope, cross-react to a non-human ortholog, lack binding to paralogs, and survive the rigors of the stringent drug development process ( 6). The processes of in vivo sequence diversification, antigen-driven somatic hypermutation, and numerous quality control checkpoints ensure the non-random selection and enrichment of B cells that produce antibodies with therapeutically desirable properties ( 2– 5).ĭespite the demonstrated successes of transgenic platforms, researchers face significant challenges related to the increasing complexity of functional design goals and targets. Antibody generation in vivo offers several advantages, including the ability to readily recover molecules that bind to the target antigen with high specificity and affinity ( 1). The remarkable capacity of engineered animals to utilize human antibody sequences to functionally replace their own has allowed researchers to harness the power of the natural humoral immune response. In this perspective, we describe some of the strategies and considerations we use for manipulating the immune systems of transgenic animal platforms (such as XenoMouse ®) with a focus on maximizing the diversity of the primary response and steering the ensuing antibody repertoire toward a desired outcome. These challenges have been met with a number of novel approaches focused on the generation of large, high-quality, and diverse antibody repertoires. While the clinical success of fully human monoclonal antibodies derived from transgenic animals is well established, recent trends have seen increasingly stringent functional design goals and a shift in difficulty as the industry attempts to tackle the next generation of disease-associated targets. The observation that the immune systems of these animals are able to recognize and respond to a wide range of therapeutically relevant human targets has led to a surge in antibody-derived drugs in current development. The creation of transgenic animal platforms expressing human antibody repertoires has revolutionized therapeutic antibody drug discovery.
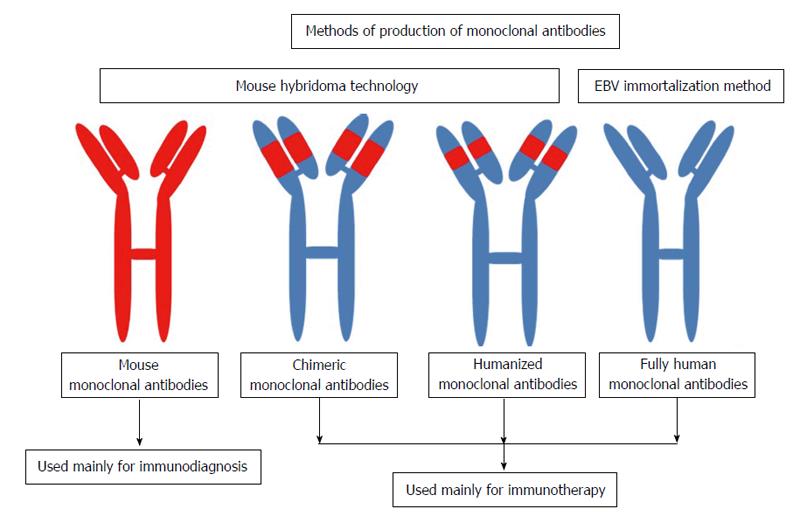
Although the predominant transgenic host species has been mouse, the genomes of rats, rabbits, chickens, and cows have also been modified to express human antibodies. While the engineering details differ, these platforms share the ability to raise an immune response that is comprised of antibodies with fully human idiotypes. Increasingly, therapeutic antibodies are discovered using transgenic animal systems that have been engineered to express human antibodies. Therapeutic molecules derived from antibodies have become a dominant class of drugs used to treat human disease.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
